Questions
Good morning to all. Now I'm trying to develop quantification method for lysine aescinate injection by HPLC. Lysine peak in not eluting. If someone knows about these method parameters, please help me.
it can’t be detected on uv detector
are using uv detector ?
Primesep 100 column with UV 210 nm it is working only lysine standard.
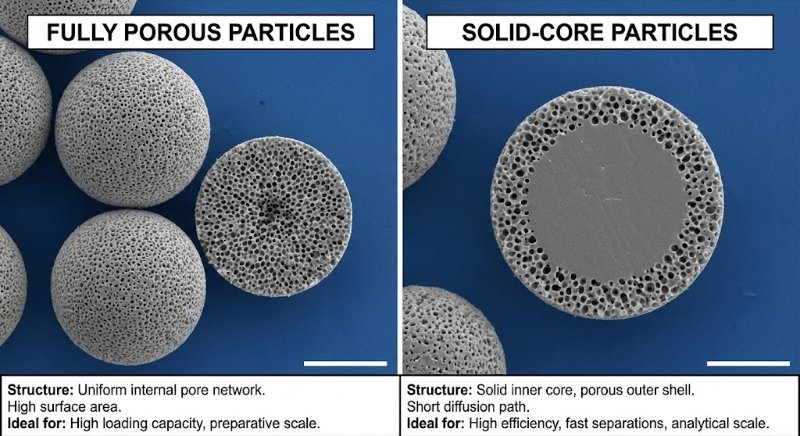

The Problem: The Pressure vs. Efficiency Trade-off
Totally Porous Particles (The Old Standard): These are like "sponges" or "Nerf balls"—pores go all the way through. To get better separation (efficiency), you need smaller particles.
The Trap: As you shrink the particle size (e.g., from 3.5 µm to 1.8 µm) to sharpen peaks, the backpressure skyrockets (often quadruples). Standard HPLC instruments (max ~6000 PSI) cannot handle the pressure required by these sub-2 micron particles.
The Solution: Superficially Porous Particles (SPP)
Also known as Core-Shell or Porous-Shell particles, these offer a "best of both worlds" solution:
The Structure: They have a solid, non-porous core (like a glass marble) coated with a thin porous shell.
Example: A 1.7 µm solid core + a 0.5 µm porous shell = 2.7 µm total particle size.
Why It Works:
Lower Pressure: The pump "sees" a larger 2.7 µm particle, keeping backpressure low enough for standard HPLC instruments.
Higher Efficiency: The sample molecules only have to diffuse through the thin outer shell (short diffusion path). This mimics the physics of a much smaller (~1 µm) particle.
Key Takeaway
Superficially porous columns allow you to achieve UPLC-level efficiency (sharp peaks) using standard HPLC hardware (lower pressure).
No answers yet.
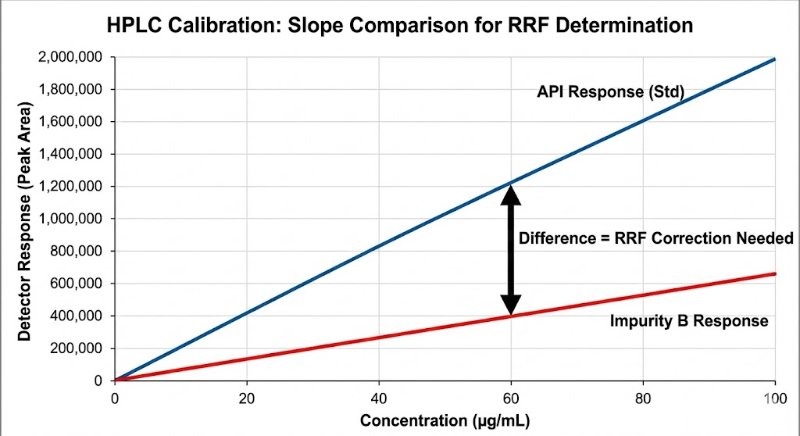
In HPLC analysis, the biggest lie a chromatogram can tell you is that "bigger peak = more amount."
We all know that different molecules interact with detectors differently. Yet, assuming a Relative Response Factor (RRF) of 1.0 for impurities is still a common shortcut that can lead to dangerous under- or over-estimation of toxic impurities.
Why RRF Determination is Non-Negotiable:
Chromophore Differences: Just because it’s an isomer doesn’t mean it absorbs UV light the same way.
Wavelength Sensitivity: An RRF valid at 254 nm might be completely wrong at 210 nm.
Regulatory Impact: ICH guidelines (Q3A/Q3B) often require correction factors if the response differs by more than 10-20% (0.8–1.2).
The "Slope Method" Gold Standard: To get a true RRF, avoid the single-point check. You need to compare the slopes of the linearity curves (Impurity vs. API) to rule out matrix effects and intercept bias.
RRF = Slope (Impurity) / Slope (API)
If you aren't correcting for response factors, are you really quantifying? Or are you just guessing?
How does your lab handle RRFs for unknown impurities? Do you default to 1.0 or run full slope-method determinations?
No answers yet.

Sustainability in the lab is no longer just a buzzword—in 2025, it’s a necessity. With rising solvent costs and stricter waste regulations, Green Chromatography is becoming the new gold standard in pharmaceutical R&D and QC.
3 Trends defining the Green Shift:
Solvent Swaps: We are seeing successful validations replacing traditional solvents like Acetonitrile and Methanol with greener, bio-renewable alternatives like Ethanol and Dimethyl Carbonate (DMC).
Miniaturization: The shift to micro-LC and nano-LC is cutting solvent consumption by up to 90% without sacrificing resolution.
Core-Shell Efficiency: Using sub-2 µm core-shell particles to speed up runs and drastically reduce mobile phase usage.
It’s not just about saving the planet; it’s about saving the budget.
Call to Action: What’s the biggest challenge you face in making your methods greener? Let's discuss in the comments. ?
#GreenChemistry #HPLC #Sustainability #Laboratory #PharmaRD #GreenHPLC #AnalyticalChemistry #2025Trends
No answers yet.
Suggest Mobile Phase for Sertraline HCl Impurity Method for, with good separation between "USP Sertaline HCl Racemic Mixture and Sertraline HCl".
No answers yet.
Required naproxen sodium Assay Alternate method in UV Spectro.
Diluent=?
UV spectro parameters=?
Hi
Diluent:dissolve 13.6 g KH2PO4 in 2000 ml water and adjust pH to 6.8 with NaOH.
Standard Solution:
25 mg of Naproxen in 50 ml, first add 5 ml Methanol and add Diluent to 50ml. after that 5 ml of this solution transfer to 100 ml and fill with water.
Test solution:
weight Equivalent 250 mg naproxen in 100 ml, add 5 ml Methanol to Dissolve Naproxen after that add diluent to volume 100ml.then transfer 1ml of solution to volumetric flask and add water to volume 100.
Blank is water.
wavelength: 263nm
During batch file run after five std. Run pressure drop occurs due to which shift in RT. How can we file an incident report. What reason and explanation and remedies we file
Is there any source of leak detected ?
✅ Incident Report – HPLC Pressure Drop & RT Shift
1) What happened (Incident Description)
During a batch sequence, after the injection of five standards, a sudden pressure drop occurred in the HPLC system. Following the pressure drop, a shift in retention time (RT) was observed for subsequent standard injections and samples. The batch was stopped, and the issue was investigated.
✅ 2) Probable Cause(s)
A) Partial blockage dislodged → sudden flow increase → pressure drop
Sometimes a partially clogged column, guard column, or inline filter gets cleared suddenly.
When the blockage clears, backpressure drops and retention times shift to lower RT because of increased actual flow.
B) Leak in the system
A loose fitting, worn ferrule, or micro-leak in pump head or column inlet can reduce pressure.
Leak causes unstable flow → RT shift.
C) Pump malfunction / air bubble
Air bubble entering pump head reduces pressure and flow.
Causes inconsistent RT.
D) Mobile phase composition shift
Sudden change in gradient accuracy due to pump mixing issue.
Leads to RT drift and pressure change.
✅ 3) Explanation (Technical Justification)
HPLC pressure is directly linked to flow resistance across the column.
A sudden pressure drop indicates reduced flow resistance, typically due to:
Clearance of blockage,
Leak formation, or Pump instability.
Retention times shifted because the actual flow rate changed even though set flow seemed unchanged.
This directly impacts chromatographic performance and validity of the batch.
✅ 4) Remedies / Corrective Actions (CA)
You can list these:
1. Checked entire fluidic path (inlet filter → pump → mixer → injector → column → detector) for leaks.
2. Tightened all fittings and replaced worn ferrules.
3. Purged pump thoroughly to remove air bubbles.
4. Flushed column with strong solvent (e.g., 100% organic) to remove particulate blockage.
5. Cleaned / replaced guard column or inline filter if excessive debris was found.
6. Verified flow rate accuracy using a volumetric flask test.
7. Re-equilibrated column and re-injected system suitability standards.
8. Ensured no further pressure fluctuations before re-running batch.
✅ 5) Preventive Actions (PA)
Regular cleaning of inline filters.
Scheduled column maintenance (backflushing if allowed).
Strict filtration of mobile phase & samples through 0.22 µm filters.
Routine pump maintenance (seal wash, piston seal inspection).
Daily leak check before starting
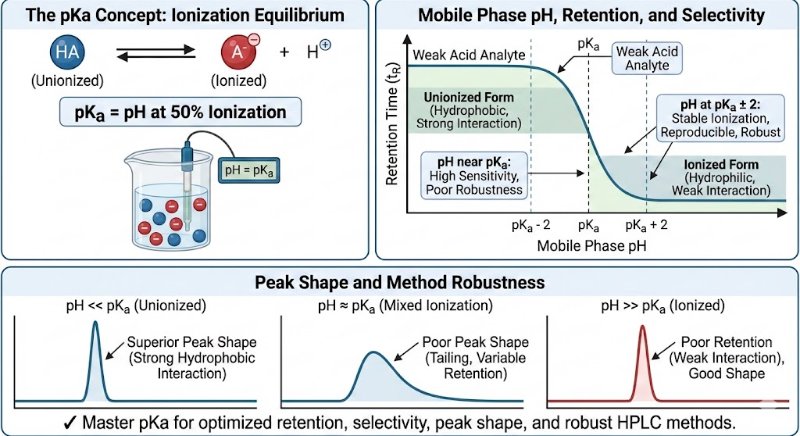
In analytical method development, particularly for analyzing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and their impurities, the pKa value of a compound is a fundamental parameter.
Why is pKa so vital?
The pKa value is the specific pH at which a molecule exists in a state of equal equilibrium between its ionized and unionized forms (50% ionized, 50% unionized). This balance is crucial because the ionization state directly dictates how a compound interacts with the HPLC system, influencing its retention time, selectivity, and overall peak shape.
Key Applications of pKa in Optimizing HPLC Methods
Strategic Mobile Phase pH Selection:
Choosing a mobile phase pH relative to the analyte's pKa is essential for controlling its ionization state and, consequently, its retention and resolution.
General Guideline: For stable ionization and reproducible chromatography, it is recommended to work at a pH that is at least 2 units away from the pKa value (pKa ± 2).
Achieving Superior Peak Shape:
The unionized form of a compound is typically more hydrophobic, allowing for stronger interactions with the stationary phase. This results in sharper, more symmetrical peaks.
Conversely, the ionized form is more hydrophilic and often shows poor retention, leading to undesirable broad, weak, or tailing peaks.
Improving Selectivity Between Analytes:
Compounds with different pKa values can be effectively separated by fine-tuning the mobile phase pH.
Even small adjustments in pH can significantly enhance resolution and selectivity, facilitating the separation of closely eluting peaks.
Ensuring Method Robustness:
A method operating at a mobile phase pH close to an analyte's pKa is highly sensitive to minor pH fluctuations. This can lead to inconsistent retention times and affect system suitability.
Working at a pH away from the pKa makes the method more robust and less susceptible to these small variations.
✔ In Summary: The pKa is more than just a number; it is a powerful guiding tool. By making pKa-driven decisions, analytical scientists can optimize retention, improve selectivity, prevent peak tailing, and ensure the robustness of their HPLC methods, ultimately leading to faster development and more reliable results.
No answers yet.
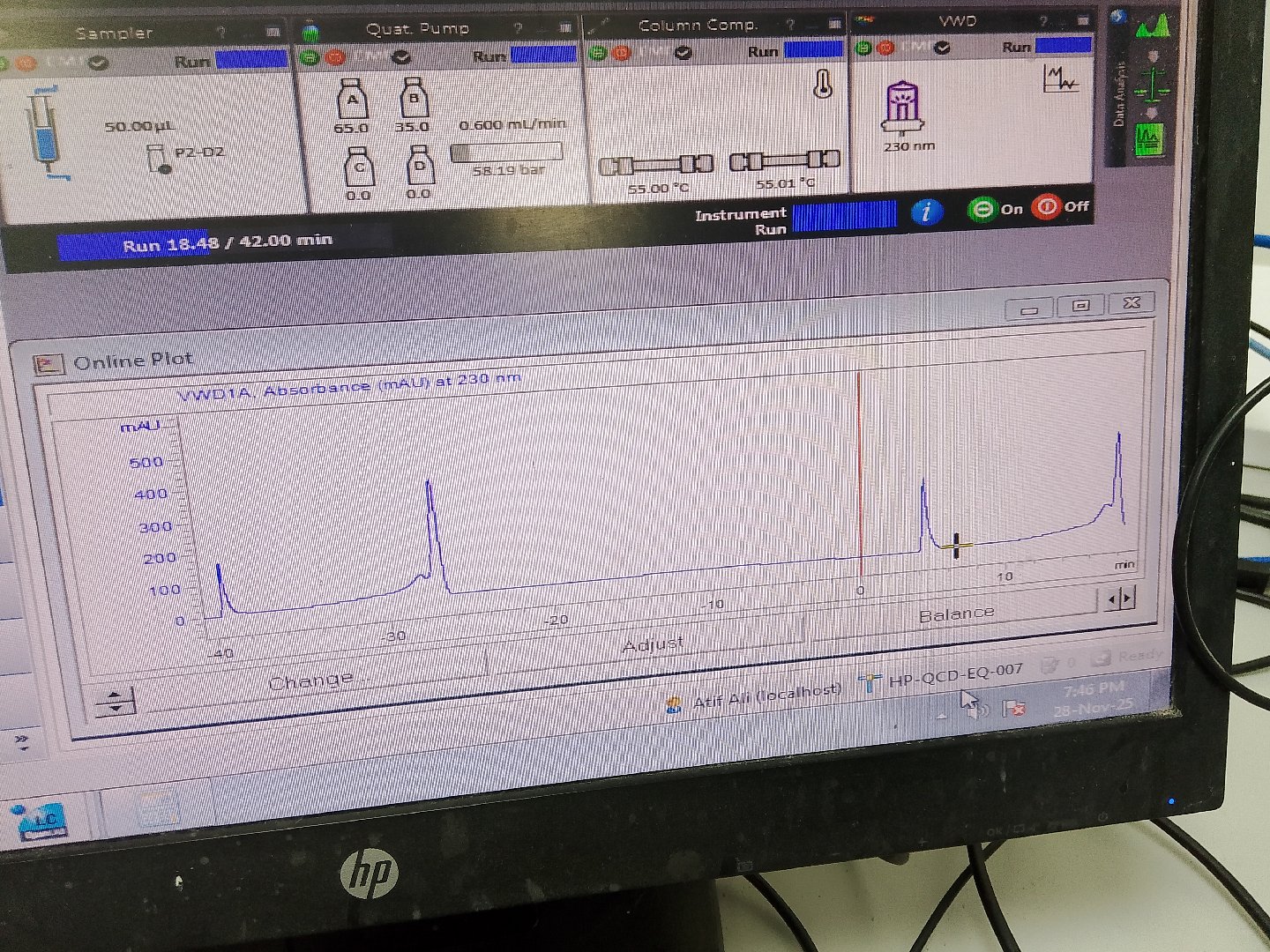
Want to remove this hump / behavior.
System is time gradient. Diluent is acetonitrile.
Suggestions please..??
if you can use the same diluent as your starting mobile phase composition
Please inform me of UV calibration with total perameter and it's procese
In general, several parameters in UV-Vis and HPLC calibration include:Wavelength accuracy, Wavelength linearity, Noise & drift
Suggest Mobile:
Composition isocrated / Gradient for
Oteseconazole:SHR8008X:SHR8008JA retention time with good separation.
Based on the chemical properties of Oteseconazole (VT-1161)—which is a tetrazole-based antifungal agent containing pyridine and fluorinated phenyl rings—and typical separation strategies for its related impurities (SHR8008 series), here is a robust starting point for HPLC method development.
Since specific impurity codes like SHR8008X and SHR8008JA are often proprietary manufacturing intermediates or degradation products, a Gradient Method is strongly recommended over an isocratic one to ensure you capture both early-eluting (polar) and late-eluting (non-polar) impurities.
Recommended Gradient Method (Best for Impurity Profiling)
This method utilizes a C18 column with a standard acidic buffer to suppress ionization of the basic nitrogen atoms found in Oteseconazole, ensuring sharp peak shapes.
Chromatographic Conditions:
Column: C18 Column (e.g., Agilent Zorbax Eclipse Plus or Waters XBridge), 150 x 4.6 mm, 3.5 um or 5 um.
Flow Rate: 1.0 mL/min
Detection (UV): 210 nm (for detecting impurities with weak chromophores) or 260 nm (more specific to the drug).
Column Temperature: 30^\circ\text{C} - 40^\circ\text{C}
Mobile Phase Composition:
Mobile Phase A: 0.1% Orthophosphoric Acid (H_3PO_4) in Water OR 10mM Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate (KH_2PO_4) adjusted to pH 3.0.
Mobile Phase B: Acetonitrile (ACN).
Time (min) Mobile Phase A (%) Mobile Phase B (%) Purpose
0.0 70 30 Initial hold for polar impurities
5.0 70 30 Isocratic hold
25.0 10 90 Linear ramp to elute Oteseconazole & hydrophobic impurities
30.0 10 90 Wash step
30.1 70 30 Return to initial
35.0 70 30 Re-equilibration
Alternative Isocratic Method (For Quick Assay)
If you require an isocratic method specifically (though less effective for separating complex impurities like SHR8008X/JA), try this composition.
Composition: Buffer : Acetonitrile (45 : 55 v/v)
Buffer: 0.1% Orthophosphoric acid or 10mM Ammonium Acetate (pH 4.5).
Note: If Oteseconazole elutes too quickly (near the void volume), decrease the Acetonitrile to 45% or 40%. If it takes too long, increase Acetonitrile to 60%.
Critical Considerations for Optimization
To achieve the "good separation" requested in the prompt, consider these factors if the initial run does not resolve SHR8008X from SHR8008JA:
1. pH Control is Key
Oteseconazole contains basic nitrogen atoms (tetrazole/pyridine moieties).
If peaks are tailing: Ensure your buffer pH is roughly 3.0. This keeps the basic nitrogens protonated and prevents them from interacting with unreacted silanols on the column stationary phase.
Buffer Choice: If you are using Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS), swap the Phosphoric Acid for 0.1% Formic Acid or Ammonium Formate.
2. Modifying Selectivity
If the impurities (SHR8008X and JA) co-elute with the main peak:
Change the Organic Modifier: Substitute Methanol for Acetonitrile. Methanol has different selectivity (protic solvent) compared to Acetonitrile (aprotic) and often resolves positional isomers better.
Change the Column Chemistry: If a standard C18 fails, try a Phenyl-Hexyl column. The pi-pi interactions from the phenyl column often help separate aromatic compounds like azole antifungals better than a standard alkyl chain.
3. Sample Diluent
Dissolve your sample in a mixture of Water:Acetonitrile (50:50). Avoid dissolving in 100% Acetonitrile if your starting gradient conditions are high aqueous, as this causes peak distortion (fronting).
Lots of thanks for resolve this issue.

No answers yet.

Choosing the right buffers and solvents is critical in LC-MS because the entire mobile phase directly enters the mass spectrometer. Compatibility with the ionization source (like ESI or APCI) is essential for high-quality data.
1. Why Volatile Buffers are Essential
Non-volatile salts, such as phosphate buffers, are unsuitable for LC-MS. As the mobile phase evaporates, these salts leave a residue that can:
Contaminate and clog the ion source.
Cause signal suppression.
Increase background noise.
Necessitate frequent and costly maintenance.
Volatile buffers are the solution. They provide stable pH control while being easily removed in the gas phase.
Benefits of Volatile Buffers:
High Sensitivity: They evaporate cleanly, allowing analytes to ionize efficiently without interference.
Low Background: Complete evaporation minimizes background ions, leading to a cleaner spectrum and better signal-to-noise.
System Stability: They prevent the residue buildup that plagues systems using non-volatile salts.
Common Volatile Buffers:
Ammonium Acetate (pH range ~4-6)
Ammonium Formate (pH range ~3-6)
Formic Acid / Acetic Acid (for acidic conditions)
Ammonium Hydroxide (for basic conditions)
2. Why Non-Polar Solvents Should Be Avoided
The choice of organic modifier is equally important. Non-polar solvents (like hexane or toluene) are not recommended for typical reversed-phase LC-MS for several reasons:
Poor Miscibility: Most LC-MS mobile phases are aqueous. Non-polar solvents are immiscible with water, which can cause phase separation.
Low Volatility & Unstable Spray: They do not evaporate efficiently in the MS source, leading to an unstable spray, a noisy baseline, and system contamination.
Ion Suppression: Their low dielectric constant is not conducive to good ion formation in ESI, resulting in poor signal intensity.
Safety Concerns: They often have higher toxicity and flammability.
3. Preferred Solvents for LC-MS
The most commonly used solvents are polar and volatile, such as Methanol and Acetonitrile.
These are ideal because they are:
Fully miscible with water.
Highly volatile, ensuring easy removal in the ion source.
Able to produce stable electrospray droplets, which promotes efficient ionization.
#PharmaceuticalAnalysis #MethodDevelopment #Principle #LCMS #UHPLC #HPLC #GC #GCMS #Volatile_Buffers #Non_polar_solvents #USP #IP #WHO #CDCSO #ICH #MHRA #AnalyticalChemistry #Solactivity #DrugDevelopment #Chemist #validation #science #pharma #GLP #SCIENCE #analytical #scientist #knowledge #sharing
No answers yet.
Hello everyone im conducting HAA9 analysis in water samples with SPE in LC MS/MS and im observing reduced areas of the peaks over the months. The LC works normally for other methods. Can someone has the same problem in HAA analysis? Or doing the same analysis? The LCMS is the Shimadzu 8050. Thank you!
No answers yet.
In UPLC during RP-HPLC Run with mobile phase as 0.1% TFA+ Water and 0.1%TFA+ ACN with 55 C column temp., the peak keeps shifting to wards left as the sequence continues.
What could be the reason.
Initially the for few runs the RT was consistent.
Any suggestions to look in to ?
No answers yet.
Hello
I need full course on Hplc
I know the princble
I need help in how work & troubleshooting
Hi Emad.
I am Alessandro from Italy.
I use an HPLC-MS thermo.
I can explain what I do during the analysis.
Please Provide me the Tropicamide 1% Eye Drop HPLC related substance Method of analysis and impurities limit.
No answers yet.
Best mobile phase for assay and their ratio mobile phase for better' resolution
No answers yet.
How make integration on empower for hplc
For any Empower software related questions refer their Tips guide in describes detailed information,below is linc fir same
Empower Tip: Integrating Peaks https://share.google/ewjvPgcZUKWHoFxUI

Excited to announce a powerful new feature in HPLC Calculator app ?
? Fine-tuned on real HPLC problems and solutions
? Aligned with international analytical guidelines
? Helps identify issues, suggest fixes, and optimize methods
Whether you’re facing peak shape issues, retention problems, or compliance challenges, the AI Assistant is designed to provide practical, guideline-based answers.
Available now inside the app — making HPLC analysis smarter and easier than ever!
#HPLC_Calculator
Download it now
Appstore
https://apps.apple.com/eg/app/hplc-calculator/id1600330994
Play store
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.Youhana.HPLC_Calculator
No answers yet.

